Severe flu risk as immune cells swap with age
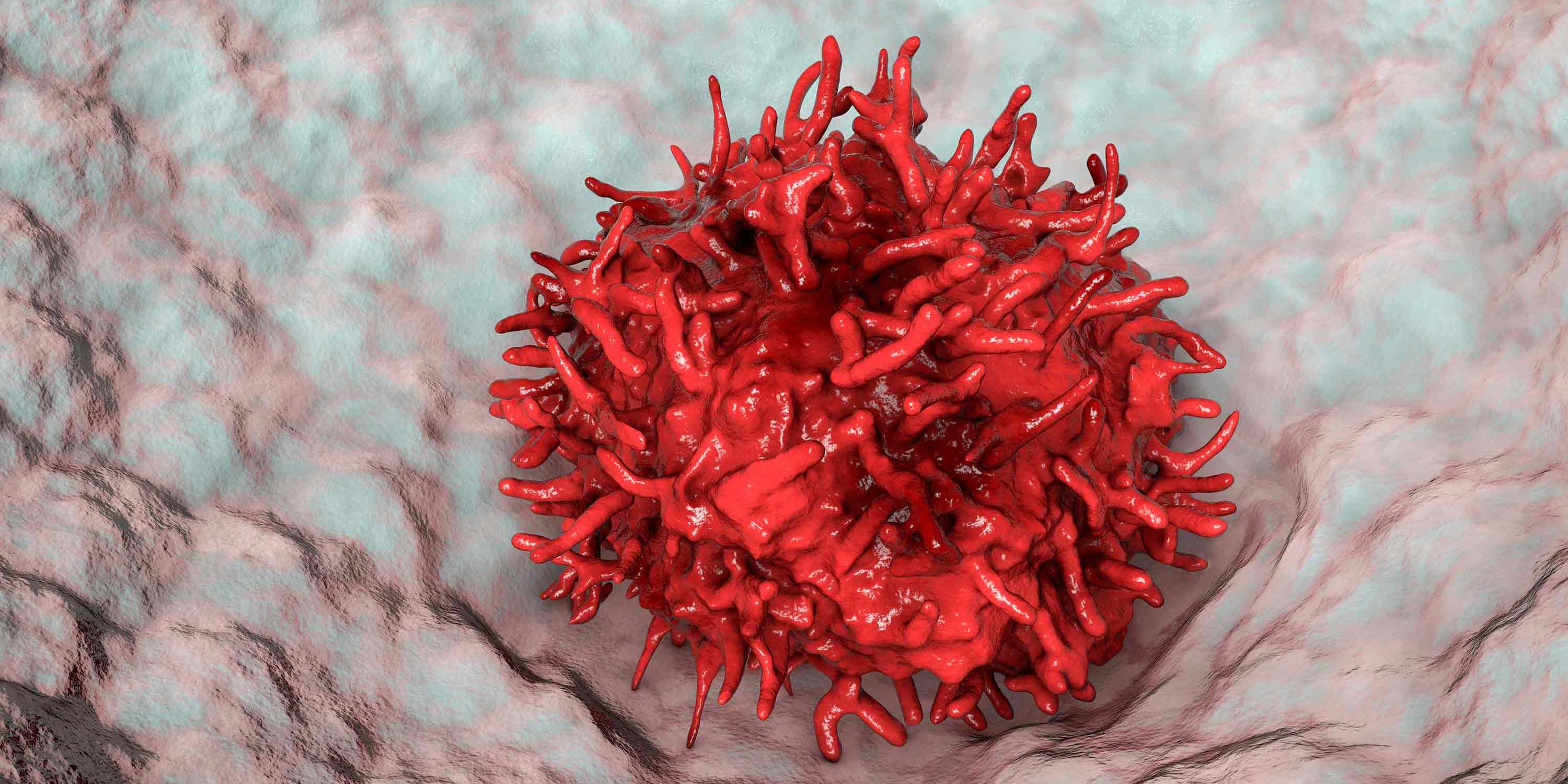
ETH researchers found that in mice, long-lived embryonic macrophages in the lungs die upon aging and during infection and are replaced by inflammatory bone marrow-derived macrophages. This causes severe disease progression when infected with viral flu.
Lung infections with the influenza virus or a coronavirus more frequently result in severe disease progression in older people. This is due to an excessive inflammatory reaction that causes damage to the lung tissue. The exact causes are not yet clear. Macrophages, also known as the immune system’s scavenger cells, play a role. They release pro-inflammatory messengers, which then trigger a severe immune response.